A new study Implementation and Analysis of Covert Channel Using iBeacon (PDF) explores the creation and analysis of covert communication channels using iBeacon, which is based on Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). Covert channels are methods used to transmit information secretly, bypassing normal security measures.
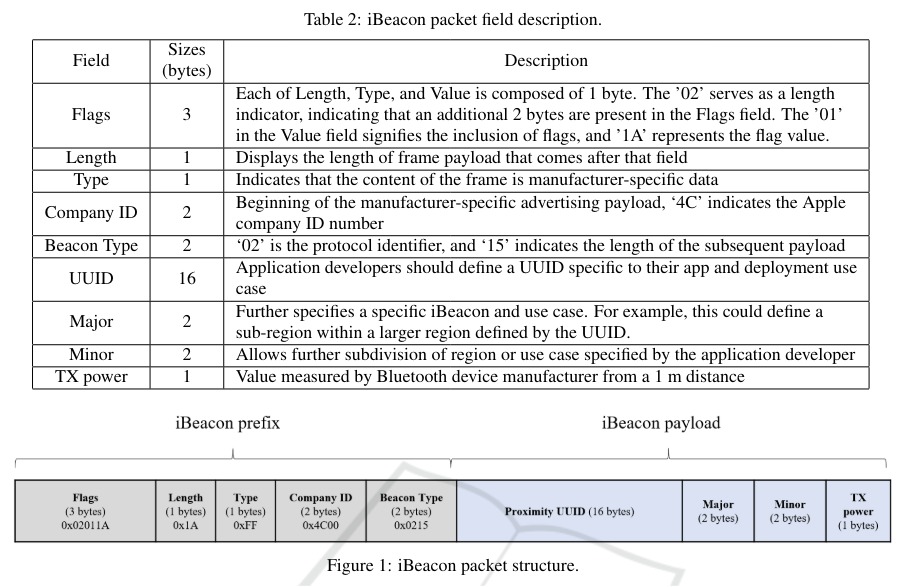
The authors introduce two types of covert channels: one that uses the payload of the iBeacon broadcast messages and another that employs the broadcasting intervals. The payload-based covert channel modifies the UUID, Major, Minor, and TX power fields of the iBeacon packets to transmit covert messages. This method achieved a maximum throughput of 911,600 Bytes per second (Bps) with a Packet Delivery Rate (PDR) consistently above 75%, indicating its efficiency in transmitting substantial data covertly.
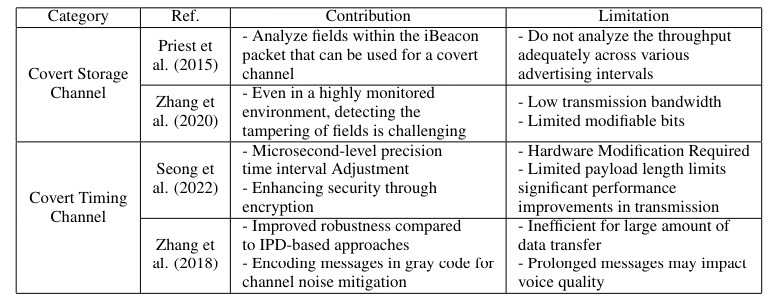
The interval-based covert channel, on the other hand, encodes messages in the time intervals between consecutive iBeacon broadcasts. Although this method provides higher concealment compared to payload-based channels, it has a lower channel capacity and can cause transmission delays.
The experimental setup involved using Raspberry Pi devices to simulate the transmission and reception of iBeacon packets, where various advertising intervals were tested. The findings highlighted that shorter advertising intervals resulted in higher throughput, with the best performance observed in the 100–200 ms range.
The study concludes by emphasising the potential for significant data transmission through BLE beacons and suggests future research to explore countermeasures against such covert channels.