Researchers at the Pusan National University, Korea have a new paper on Applying Movement Constraints to BLE RSSI-Based Indoor Positioning for Extracting Valid Semantic Trajectories.
The received signal strength (RSSI) of beacons is often used to infer location. However, the RSSI is subject to reflection and blocking from walls, people and other obstacles causing the derived locations from the raw data to be ‘jumpy’. There are many ways to process the raw data, such as Hidden Markov Models, k-nearest neighbors and Deep Neural Networks (DNN) to obtain smoother trajectories.
The researchers use movement constraints and sliding-window aggregation to extract invalid trajectories and provide real-time semantic trajectories.
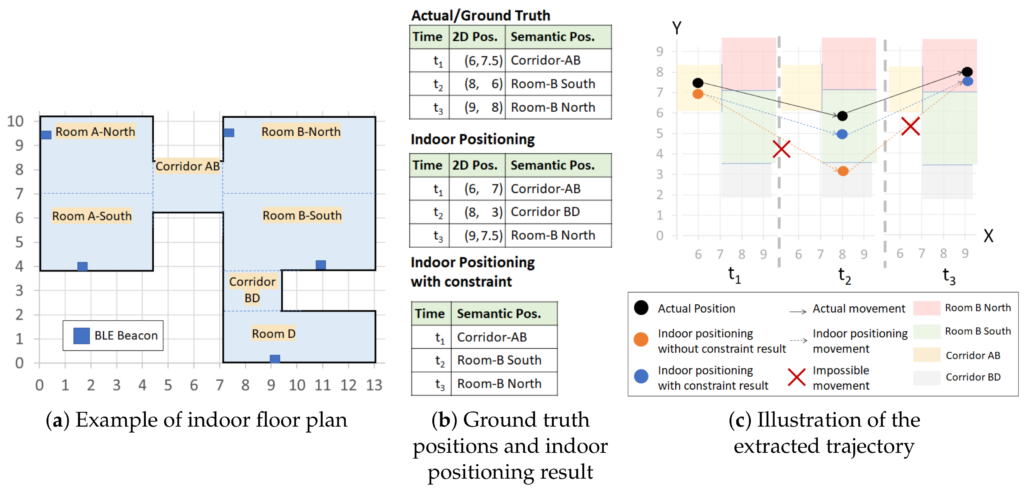
The paper shows the proposed movement constraint-based approach extracts valid trajectories that are comparable to the unconstrained and non-machine language approaches. This new approach is particularly suited to dynamic indoor environments where the reflection and blocking changes over time.