Researchers from Japan have a new Relabelling Approach to Signal Patterns for Beacon-based Indoor Localization in Nursing Care Facility. Bluetooth beacons were used in a nursing care facility to enhance the tracking and location estimation of caregivers. These beacons were strategically placed throughout the facility, particularly outside patient rooms and in common areas. The caregivers carried smartphones with a mobile application called FonLog installed, which recorded the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) readings from the beacons and logged location labels.
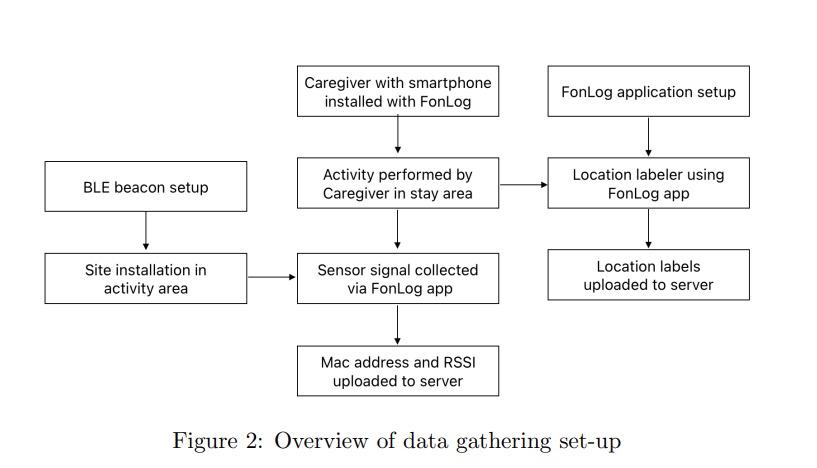
The beacons were set to a frequency of 10 Hz with a coverage range of up to five meters. The main challenge addressed in this study was the signal loss and limited data, which affected the accuracy of indoor localisation. To improve the data quality, a relabelling approach was applied. This involved observing the signal patterns in different rooms and using these patterns to augment the training data by relabelling RSSI values from one location as samples for another location with low data samples.
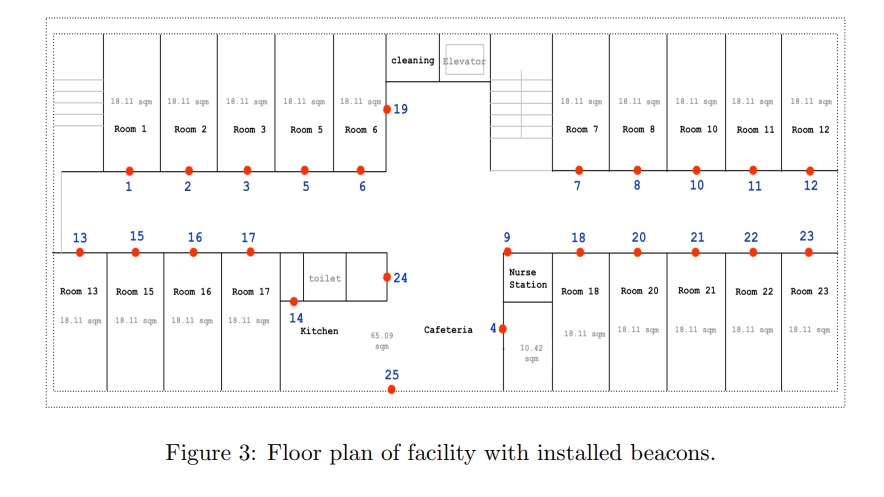
This approach aimed to increase the dataset and improve the model’s accuracy in recognising the caregivers’ locations. By doing so, the accuracy of the indoor localisation model improved, achieving an accuracy of 74%, which was a 5% improvement over the original data. The use of Random Forest for location recognition further enhanced the performance, demonstrating the effectiveness of combining relabelling with machine learning techniques for indoor localisation in a healthcare setting.