New research “Hybrid-AI-Based iBeacon Indoor Positioning Cybersecurity: Attacks and Defenses” by Wei-Tzu Hung, focuses on the cybersecurity aspects of iBeacon systems, particularly in the context of indoor positioning and navigation. iBeacon is increasingly used in very large and important public spaces for indoor navigation, using the Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) in mobile phones. However, the security of these systems is sometimes a concern, especially against cyberattacks.
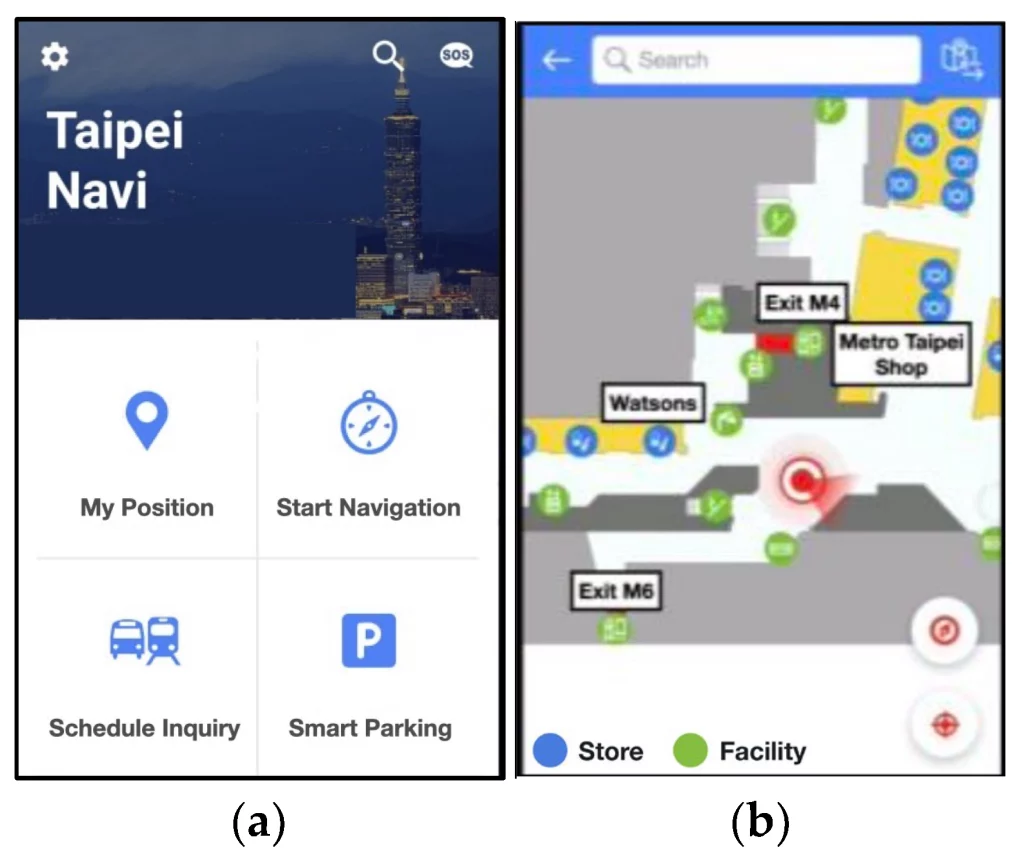
The study uses the iBeacon system at Taipei Main Station, a major transportation hub, as a case study. This station experiences a high daily traffic flow, making it a critical area for such technology. The research explores potential attacks on the iBeacon system and investigates defence technologies, incorporating AI techniques and human participation.
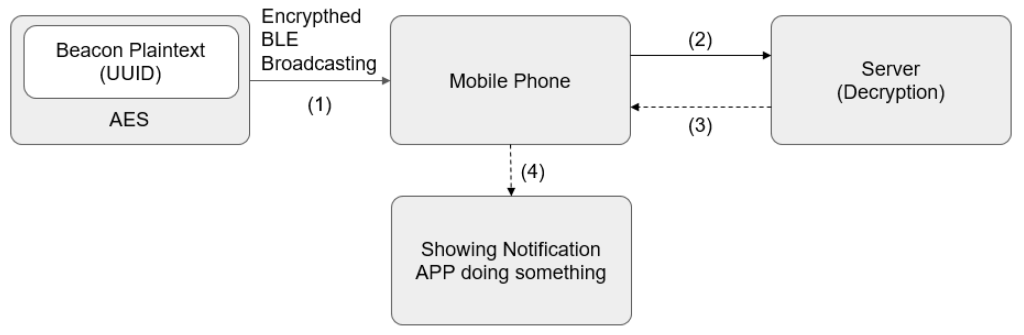
The study looks into various aspects of iBeacon technology, including its mechanisms, related work in the field and specific challenges in information security. It also discusses the design of the iBeacon system at Taipei Main Station, potential attacks by hackers and methods to defend against these attacks.
The paper concludes with insights into future studies in this area. Key findings include the necessity of incorporating information security technology and rolling coding encryption in the early stages of iBeacon system planning. These methods are currently the best defence strategies. The research suggests that rolling coding is the most cost-effective defence, but for critical infrastructure, a more secure method, such as predictable and encrypted rolling coding, can be used.