New research explores the use of game-based inquiry learning in a maritime science museum, integrating emerging technologies to enhance visitors’ learning experiences. The study introduces MUSEON, an ontology-driven game-based learning (GBL) application designed to engage visitors in guided inquiry activities about museum exhibits.
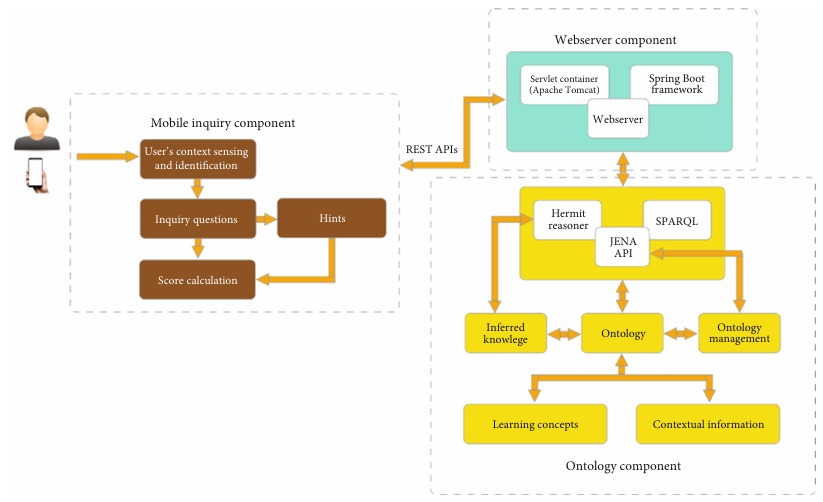
Beacons were used to enhance the contextual awareness of the learning experience. BLE beacons were strategically placed around the museum to detect visitors’ locations and provide relevant inquiry tasks and hints based on their proximity to exhibits. When a visitor entered a beacon’s range, the MUSEON application activated corresponding learning tasks, helping users engage with exhibits in an interactive and structured manner. The beacons ensured that visitors received context-specific content, allowing them to explore the exhibits dynamically rather than passively. By integrating BLE beacons with an ontology-driven learning approach, the study demonstrated how emerging technology can support situated learning and improve engagement in museum environments.
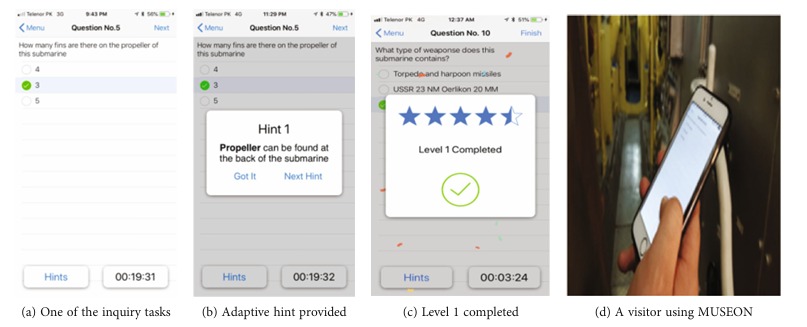
The findings indicate that visitors using MUSEON had a more engaging and effective learning experience, with 71.6% of participants expressing satisfaction with the game-based approach. The experimental group also outperformed the control group in learning assessments, scoring an average of 74.6% compared to 56.4%. The study highlights the potential of using context-aware technologies, such as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons, to facilitate location-based inquiry learning in informal educational environments like museums.