A new paper titled Evaluation of RSSI-Based Distance Estimation with ESP32 BLE Modules for Indoor Asset Tracking investigates the accuracy and reliability of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology when using Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) data for determining distances indoors. The study uses ESP32 modules due to their affordability, energy efficiency, and built-in BLE support. Experiments were carried out in three conditions: clear line-of-sight, wall obstruction and a mobile tracking scenario.
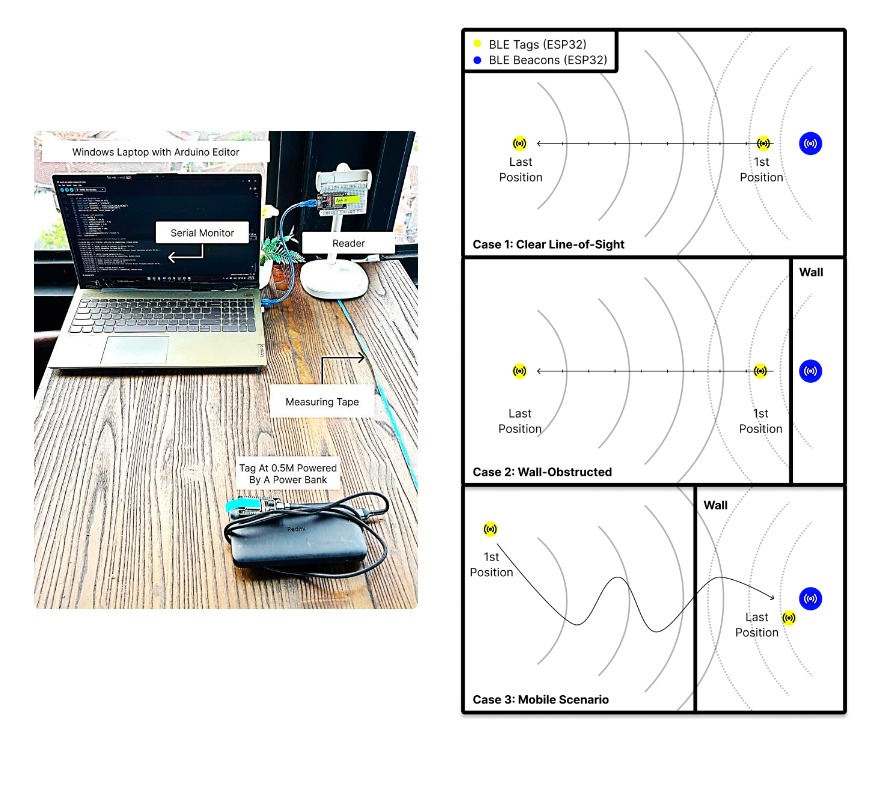
Using a log-distance path loss model with a reference RSSI of −47 dBm at one metre and a path loss exponent of 2, the authors found that the ESP32 BLE system could reliably estimate distances within four metres under line-of-sight conditions, with less than 25 per cent error. Beyond five metres, however, the signal became unstable and led to overestimation of distances, particularly in obstructed environments. A wall caused an immediate signal drop of 6 dBm even at one metre, and packet loss rose from zero per cent at short distances to around fifty per cent at 8.5 metres. Mobile tracking showed irregular RSSI jumps, making movement detection inconsistent.
The results demonstrate that raw RSSI values are too variable for accurate standalone tracking, mainly due to reflection, absorption, and interference effects. While simple to use and inexpensive, the technique is unreliable for precise positioning. The study concludes that to achieve dependable performance, especially in complex indoor settings such as hospitals or factories, more advanced methods are needed. These could include Kalman filtering, RSSI fingerprinting, or sensor fusion combining multiple BLE readers or inertial sensors. Such enhancements could reduce estimation errors from about 500 per cent to below 30 per cent over ten metres.
Overall, the research establishes a baseline understanding of the limitations of ESP32-based BLE tracking systems and provides a foundation for future work aimed at improving indoor positioning accuracy through data filtering and sensor integration.
