Too many potential customers contact us asking what’s the least expensive beacon that provides the best range, the best battery life and the smallest size. Unfortunately, all these things are related. You need a larger battery to provide enough power for a longer range. A large battery implies a larger beacon size. A larger battery and case implies a more expensive beacon. The choice of ‘best’ beacon usually involves some sort of compromise.
It’s also often the case that customers focus on price, range, battery life and size without considering other factors such as:
- Visual appearance – Good-looking beacons can sometimes be counter-productive as they can be attractive to thieves. Black ones or ones that blend into the environment work best.
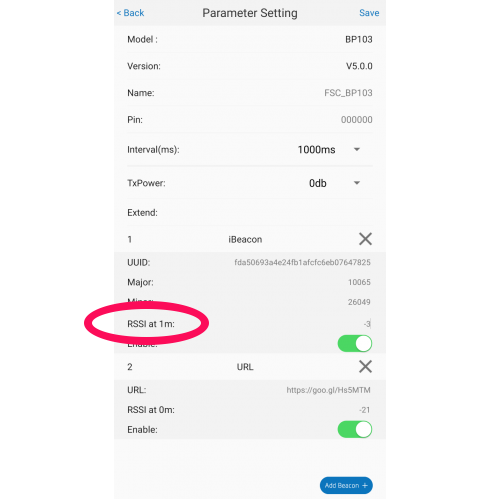
- App – Some manufacturer configuration apps are easier to use than others. We prefer KKM, Meeblue and Minew apps.
- Waterproofing – Some unexpected scenarios, such as use inside cars, need waterproofing due to high humidity.
- Motion triggering – Some beacons provide motion triggering to significantly increase battery life.
- On-off button – It’s sometimes desirable to be able to turn the beacon on and off without having to remove the battery, especially during storage.
- Attachment options – Some beacons include strong double sided stickers, tabs for screws or holes for fastening.