It’s often the case you need to know if a beacon is working and advertising the correct information. It’s also sometimes necessary to differentiate between beacons, based on their signal strength, so you know you are setting up the correct beacon. Other times, you might want to know a beacon’s MAC address.
The best scanning app is Nordic nRF Connect that’s written by the manufacturer of the System on a Chip (SoC) in most beacons. Nordic nRF Connect detects all beacons and indeed all Bluetooth LE devices, irrespective of the SoC manufacturer because it just looks for standard Bluetooth advertising. nRF Connect is intelligent in that it works out the kind of beacon and displays the appropriate type of information.
It’s important you use the Android version of nRF Connect. Due to over-zealous efforts by Apple to hide identities, it’s not possible for iOS scanning applications to see advertising iBeacon (UUID, major and minor) information nor the Bluetooth MAC address even though these are openly transmitted by beacons.
Here’s an example scan:
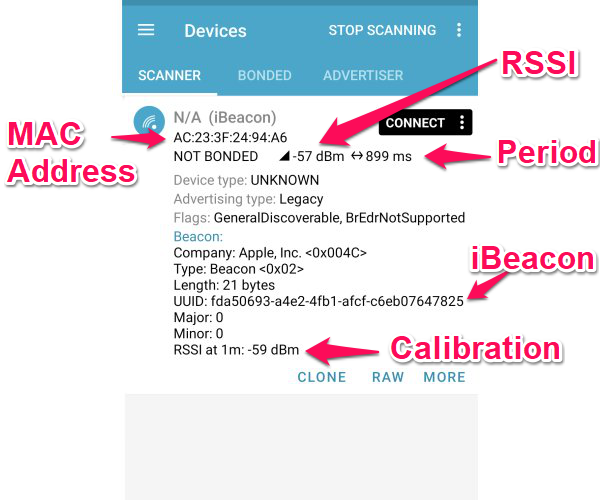
In the above screenshot you can an iBeacon that has been tapped on to show extra information. All devices have the MAC address and a Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI). The MAC address uniquely identifies the device.
Devices that scan for beacons will experience a signal strength (RSSI) that varies depending on the distance to the beacon. It’s expressed in dBm and is always negative. A more negative number indicates the beacon is further away. A typical value of -10 to -30 dBm indicates the beacon is close. A typical value of -110 indicates the beacon is near the limit of detection. You can use this to determine which beacons are closest. You usually configure beacons when they are right next to the phone and have a higher, less negative, RSSI.
nRF Connect also shows the advertising period that’s based on how often the app sees the advertising as opposed to what has been set in the beacon. The value is rarely exactly what you have set because Bluetooth requires some randomisation of the advertising period to reduce the possiblity of collisions between devices, in the vicinity, that are set to the same period. Also, being wireless, not all advertising is seen which causes jumps in the shown advertising period. Read more about choosing the advertising period.
There’s also a ‘RSSI at 1m’ which is the beacon’s self-declared value, in the advertising data, of what the RSSI should be at 1m. This can be used by scanning devices, such as apps, as a form of calibration for determining distance. In most cases this value isn’t used and should be ignored. Read more about power and the measured power calibration value.