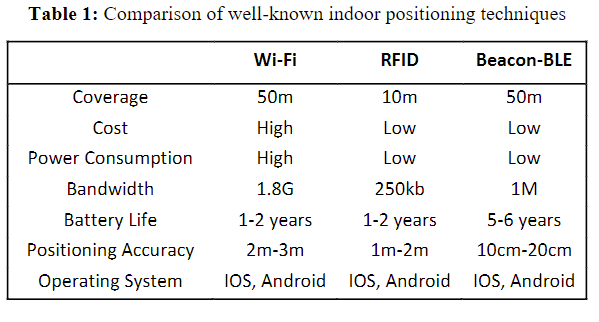
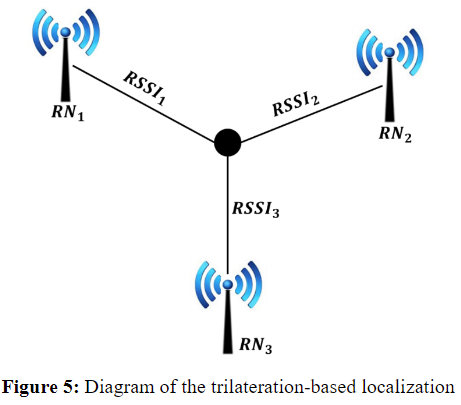
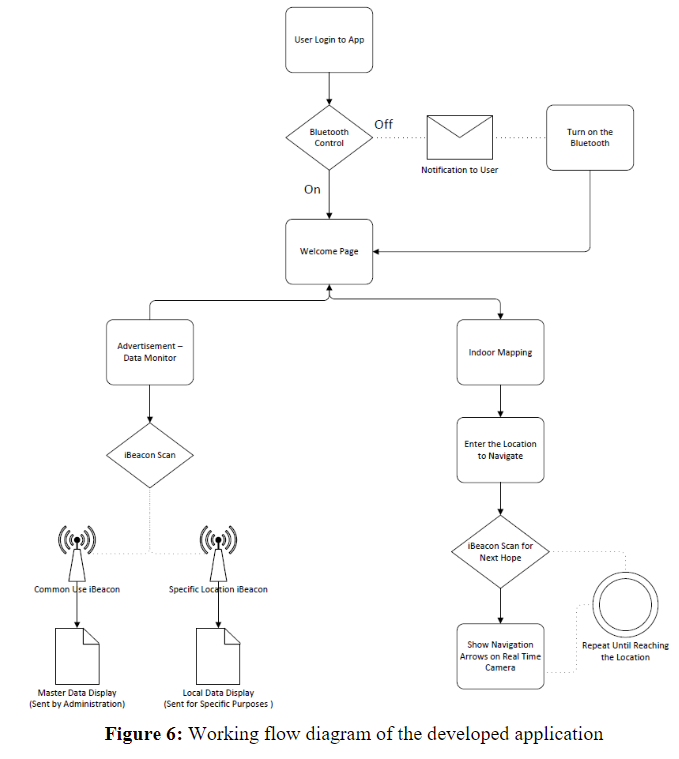
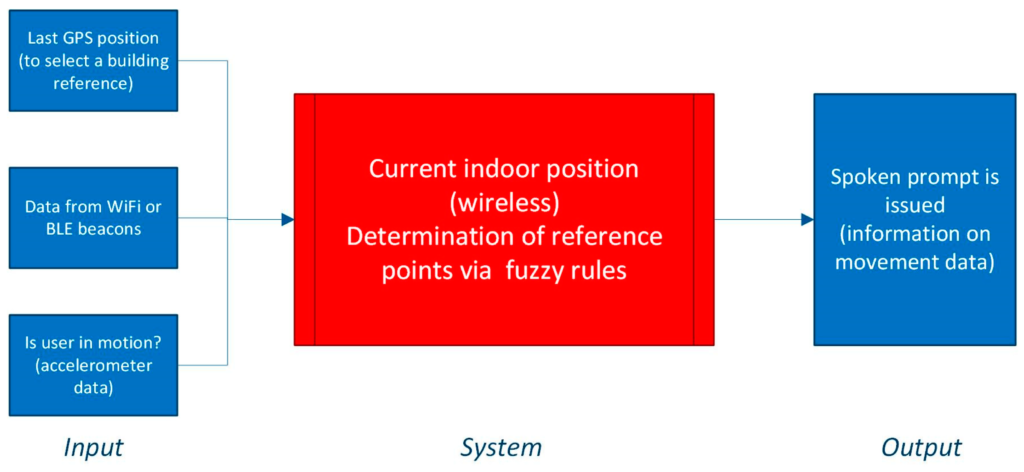
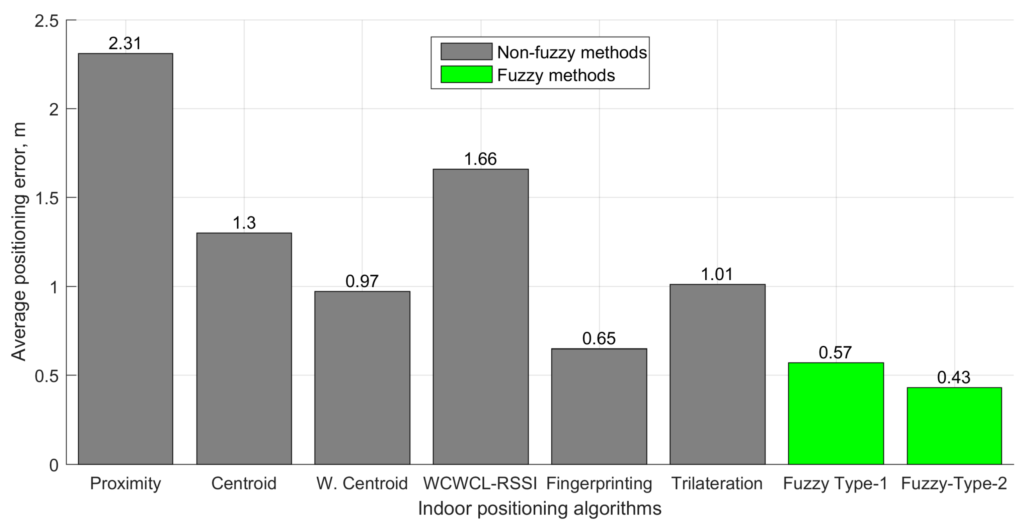
New research looks into indoor navigation systems specifically designed for environments with repetitive structures, such as cruise ships, using Bluetooth low-energy (BLE) beacons without relying on GPS. The system incorporates a mobile application that uses these beacons to guide users accurately within buildings. The system optimises navigation through the use of pre-calculated routes, which minimises data storage requirements and enhances the application’s energy efficiency.
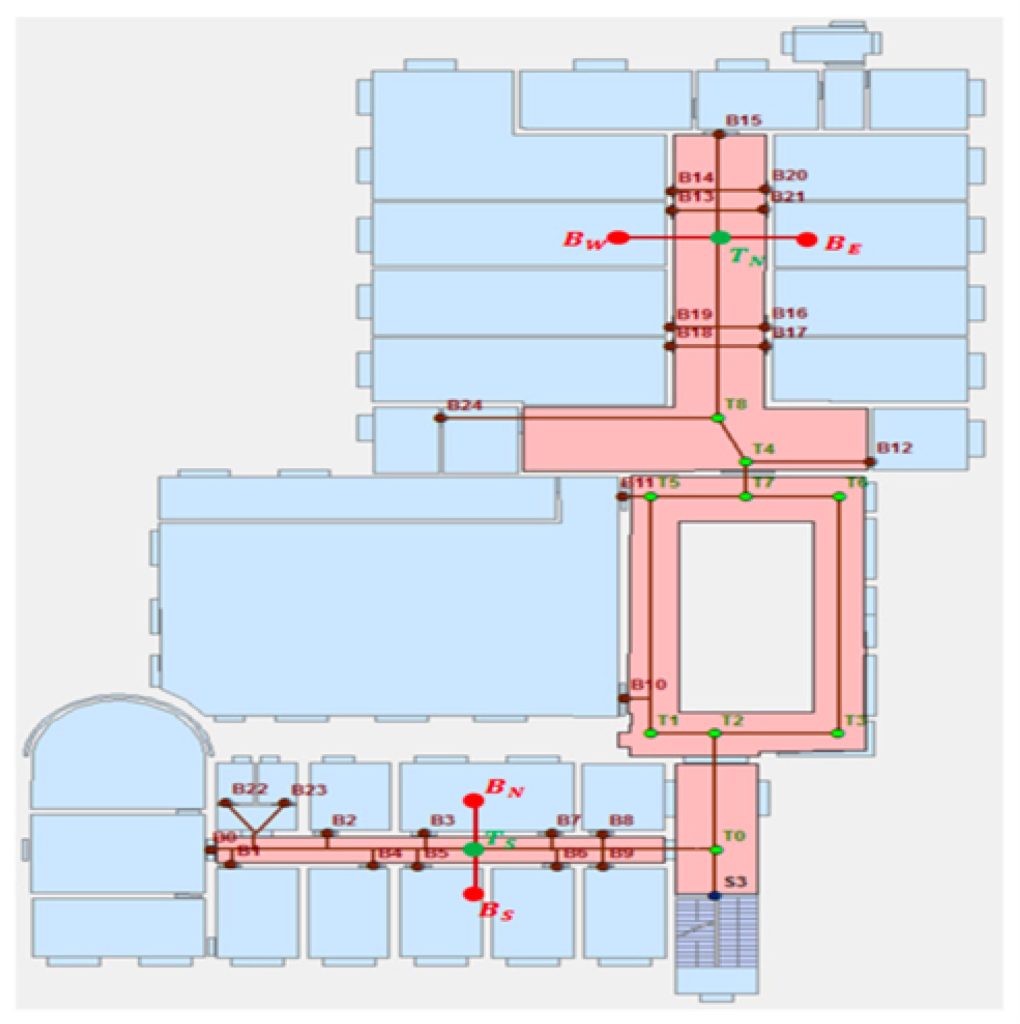
It system includes a sophisticated user interface that displays the route and updates navigation in real-time based on user movement and beacon signal reception. The implementation faced several challenges, particularly related to the synchronisation and real-time processing of beacon signals, which were addressed by optimising the beacon scanning process and the communication between system components.
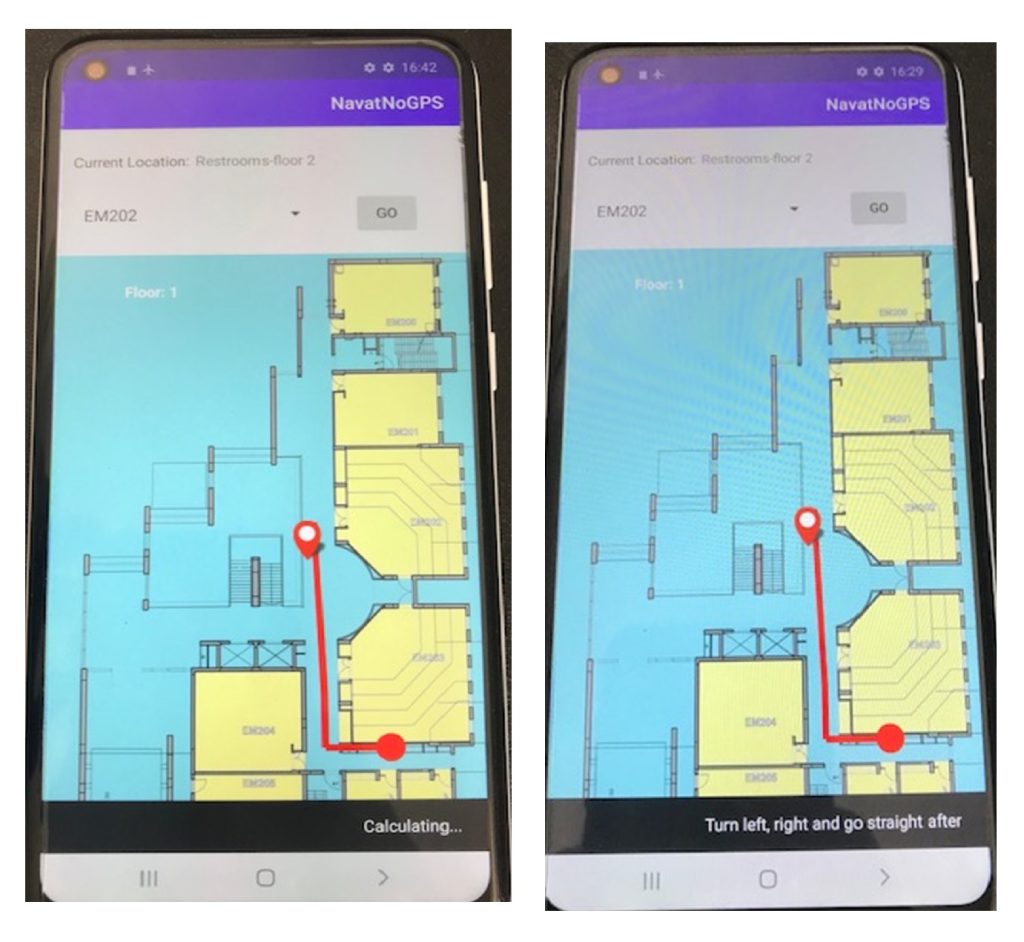
The study lays the groundwork for future exploration and deployment of indoor navigation systems that leverage repetitive architectural features for enhanced navigation efficiency.