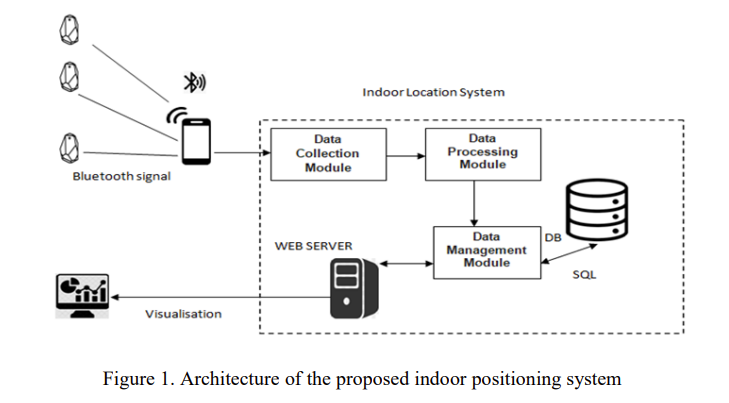
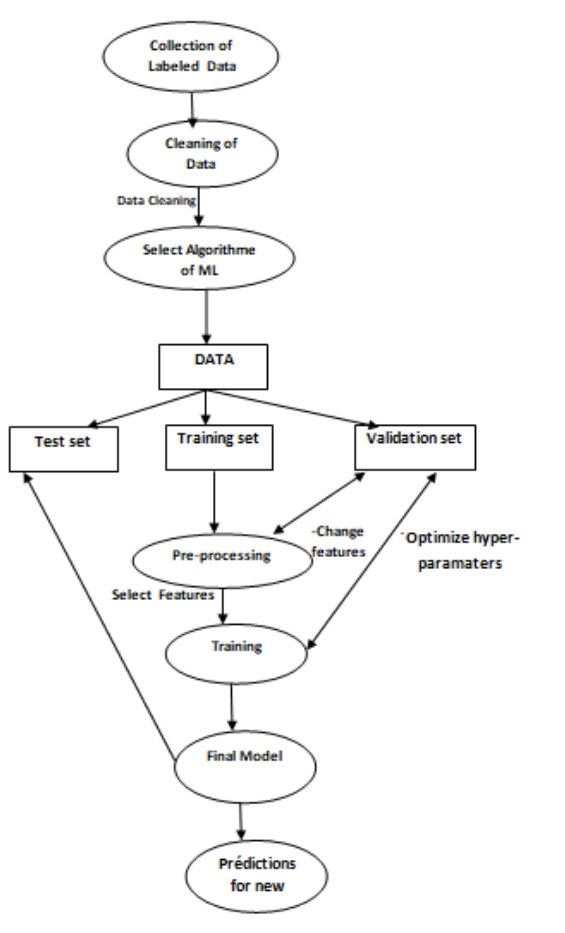
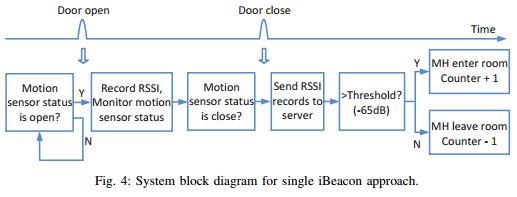
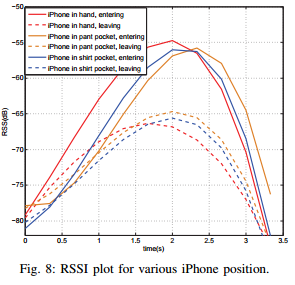
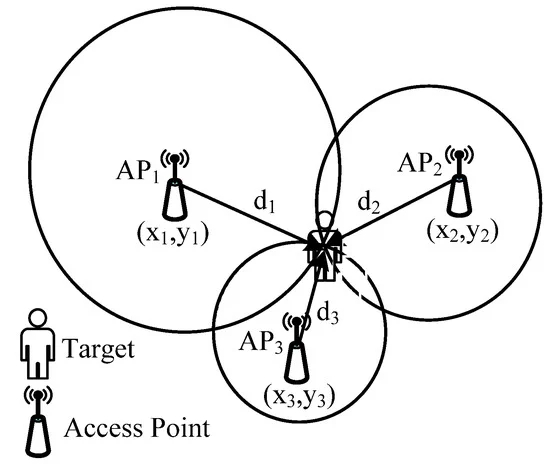
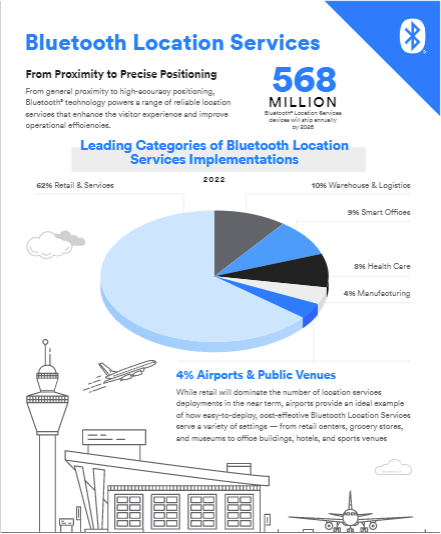
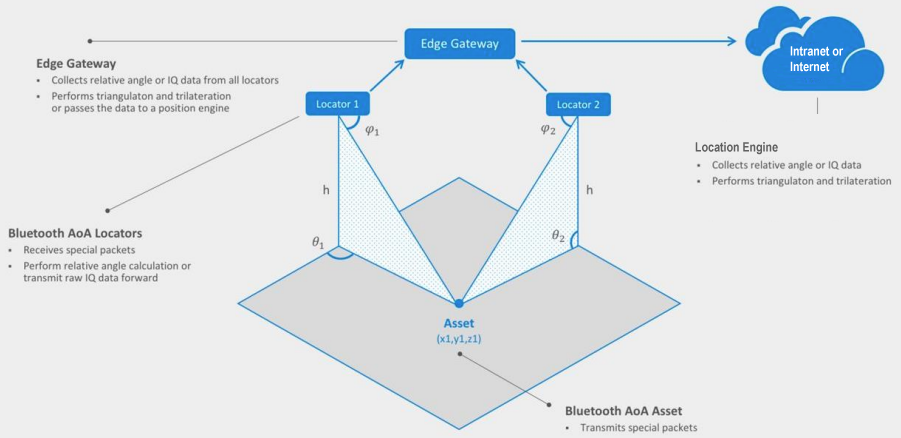
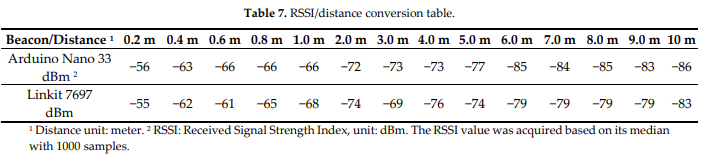
Bluetooth SIG, the organisation responsible for Bluetooth standards, has a new Bluetooth® Market Update in collaboration with ABI Research. Bluetooth covers a large range of device types and application areas. Here are some insights related to location services.
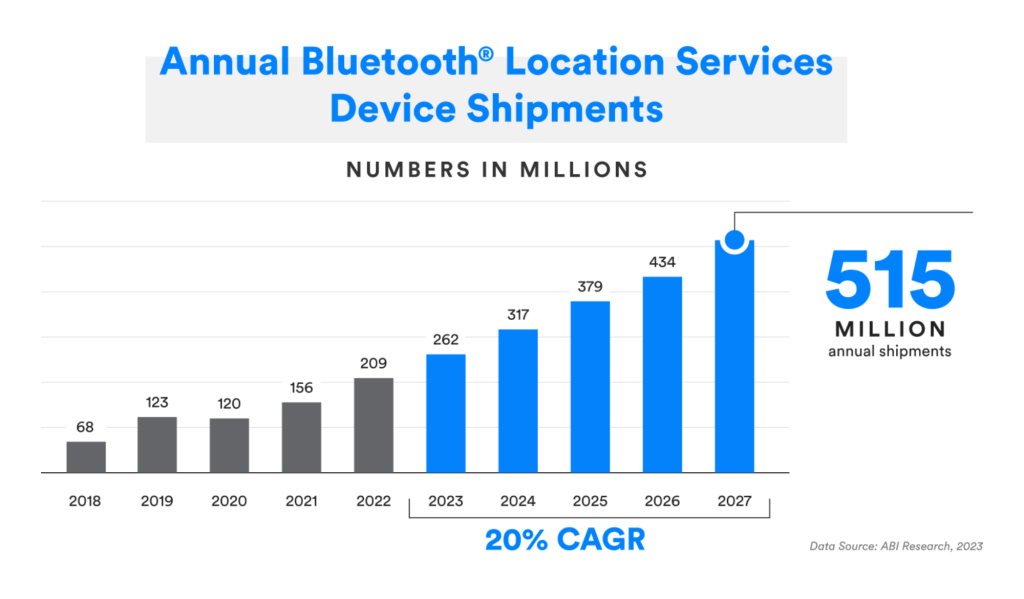
Bluetooth location services device growth will trend significantly upward and return to pre-pandemic forecasts due to heightened awareness of the benefits of Bluetooth location services. There will be 2.46x growth in annual Bluetooth location services device shipments from 2023 to 2027.
Bluetooth real time location systems (RTLS) are set for rapid growth. New regulatory and safety requirements in manufacturing, stricter compliance procedures and sustainable operation requirements are making RTLS solutions more attractive. There will be 178,000 Bluetooth® RTLS implementations by the end of 2023. Many commercial and industrial facilities are now relying on asset tracking solutions to optimise resource and inventory control. The commoditisation of off-the-shelf Bluetooth asset tracking gateways and beacons are major drivers behind continued growth. 112 million Bluetooth asset tracking devices will ship in 2023.