The great new paper titled Evolution of Bluetooth Technology: BLE in the IoT Ecosystem provides a comprehensive review of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), tracing its development from its origins to its role in the modern Internet of Things (IoT). The authors outline the historical evolution of Bluetooth, starting with its initial release in the late 1990s through to the latest version, Bluetooth 6.0, introduced in 2024.
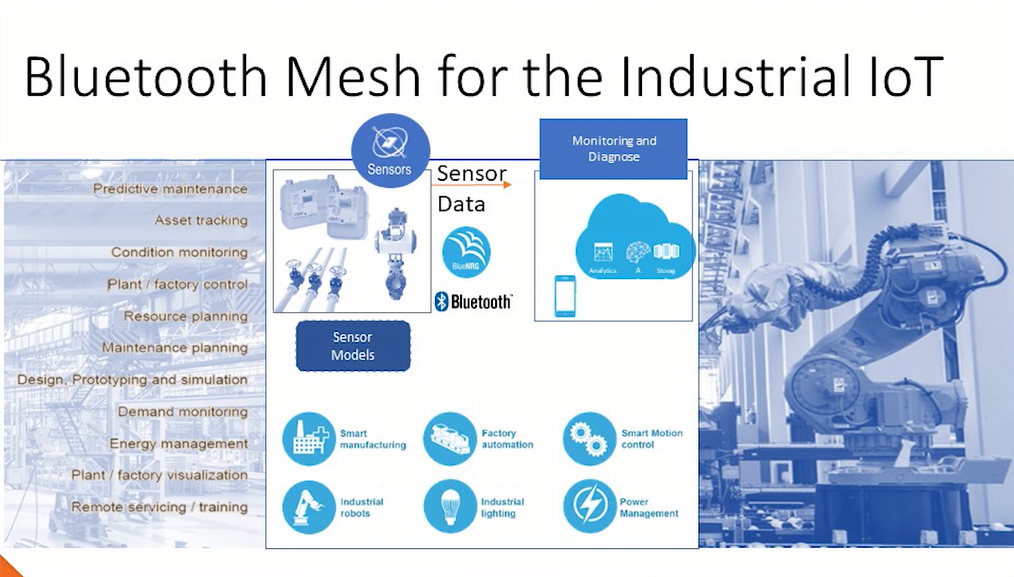
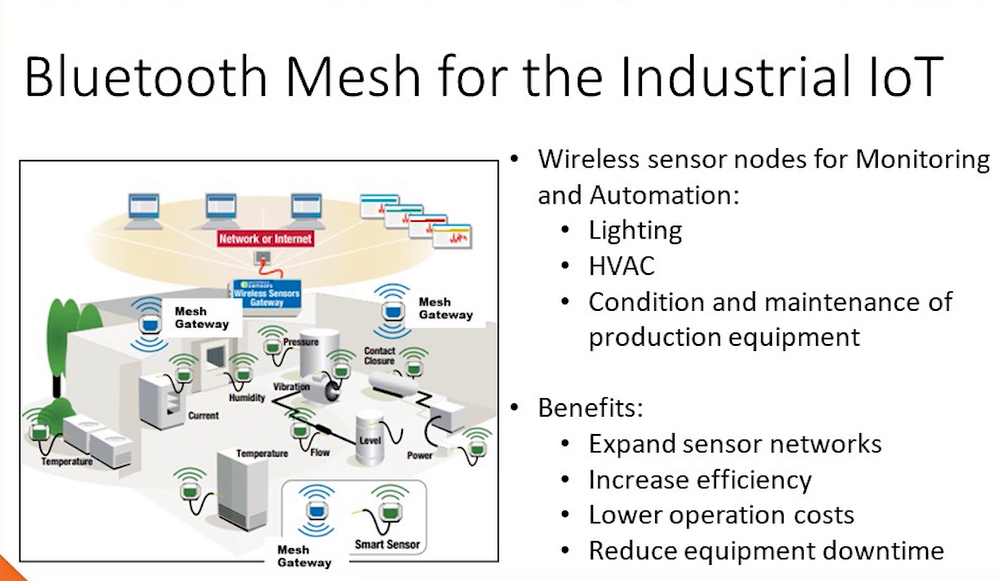
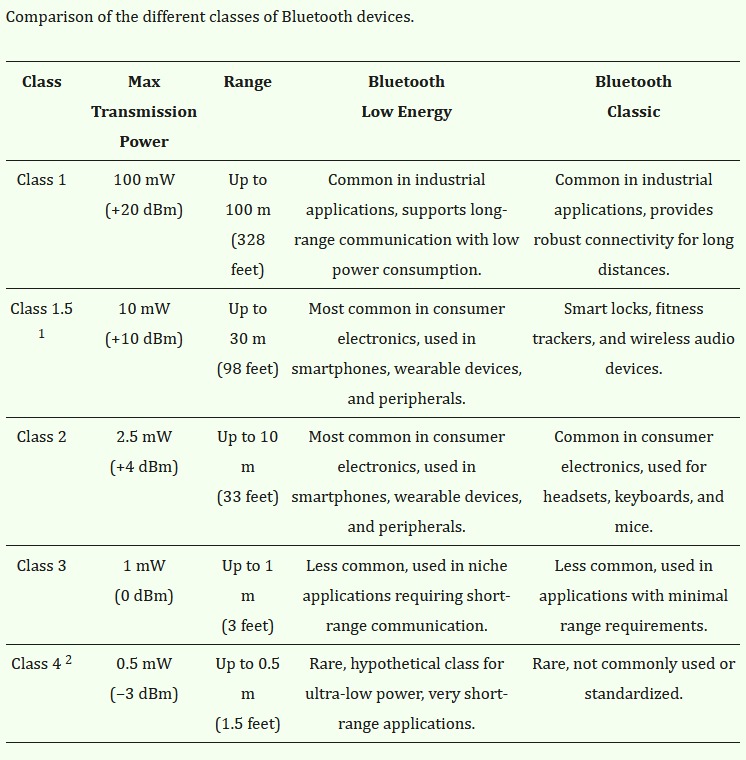
BLE, introduced in Bluetooth 4.0 in 2010, was designed as a low-power alternative to Bluetooth Classic, making it ideal for IoT applications where energy efficiency is critical. The paper discusses BLE’s technical characteristics, such as its reduced power consumption, moderate data rates, mesh networking support, and robust security features and highlights the differences from Bluetooth Classic.
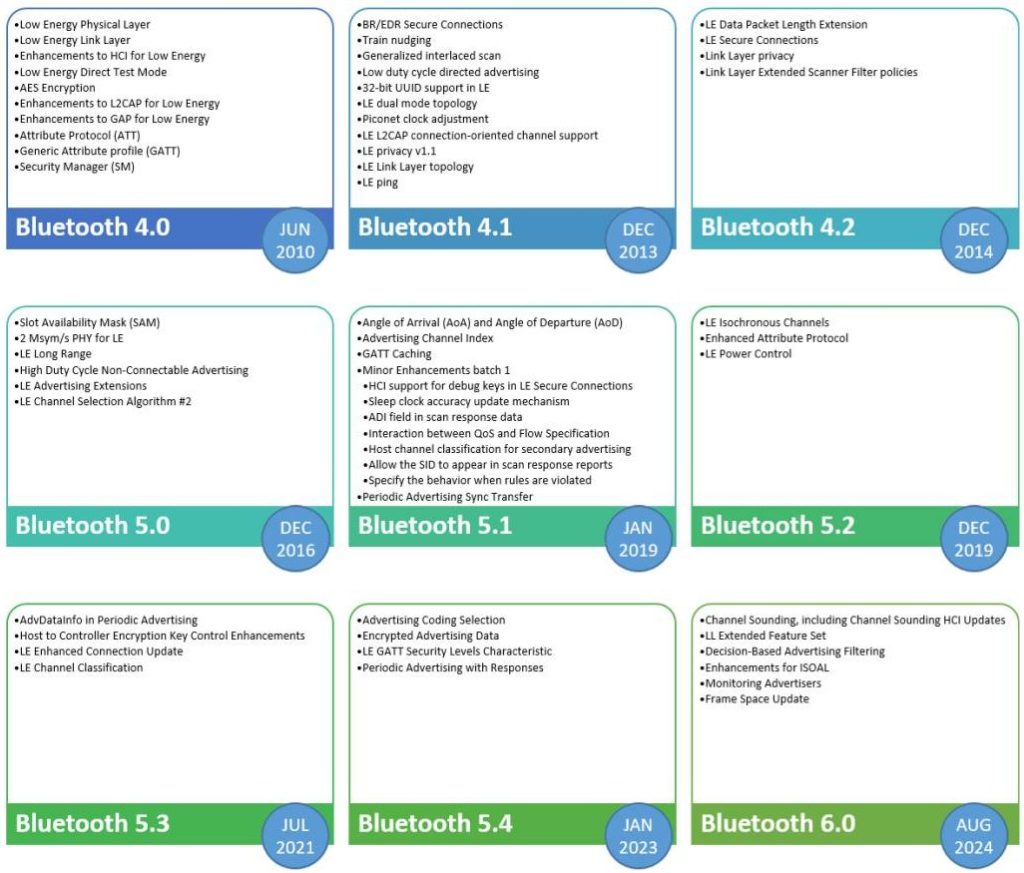
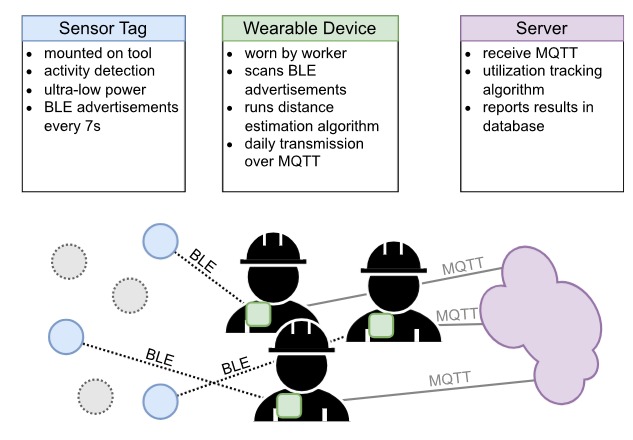
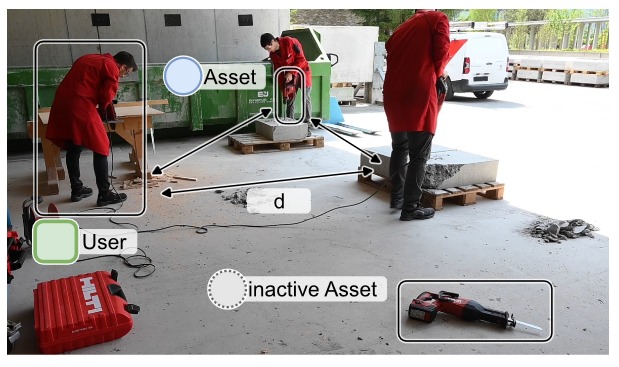
The review details the progression of BLE through its successive versions, each introducing improvements in range, throughput, latency, and security. It also explores the integration of BLE in various IoT contexts, including smart homes, healthcare, automotive, retail, industrial automation, and smart cities. Several case studies are used to illustrate real-world BLE implementations, demonstrating its utility across multiple sectors.
The paper considers BLE’s alignment with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly in promoting energy efficiency, sustainable urban development, and climate action. BLE’s role in enabling sustainable technologies, such as solar-powered IoT devices and low-power smart infrastructure, is also discussed.
Finally, the article reviews current technical challenges, such as power management, interference, scalability and security. It proposes potential solutions and anticipates future directions involving BLE’s integration with artificial intelligence, enhanced privacy protocols and expanded functionality in next-generation IoT ecosystems.