The new paper Securing the Invisible Thread: A Comprehensive Analysis of BLE Tracker Security in Apple AirTags and Samsung SmartTags by Hosam Alamleh, Michael Gogarty, David Ruddell, and Ali Abdullah S. AlQahtani, looks into the security of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) trackers, particularly Apple AirTags and Samsung SmartTags. The research identifies a broad range of attack vectors, including physical tampering, firmware exploitation, signal spoofing and cloud-related vulnerabilities. It examines the security measures and cryptographic methods used in these devices, revealing that while they provide considerable utility, they also introduce significant security risks.
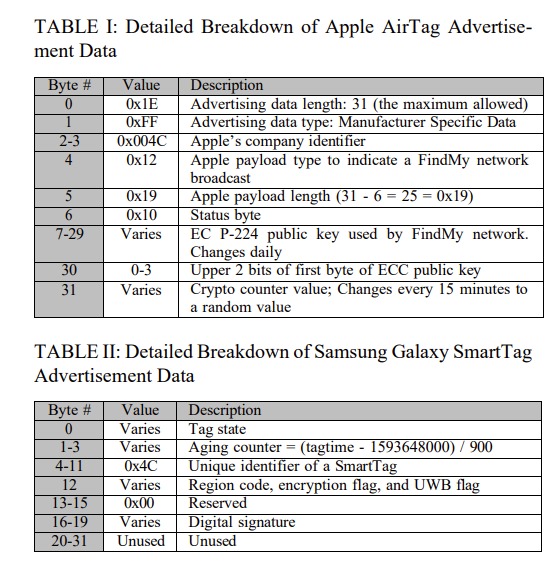
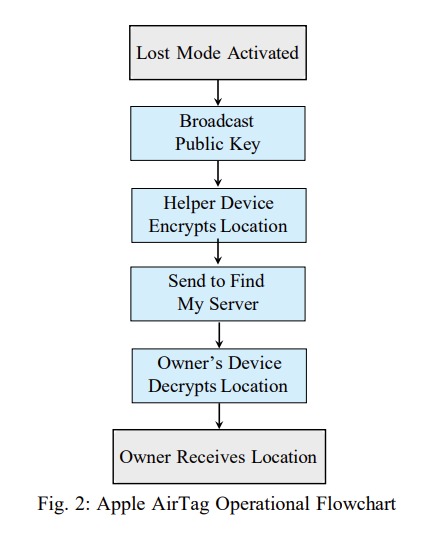
Apple AirTags and Samsung SmartTags differ in their approach to security and privacy. Apple prioritises user privacy, leading to authentication challenges and successful AirTag spoofing instances. Samsung’s design aims to prevent beacon spoofing but raises concerns about cloud security and privacy. The study highlights the trade-off between battery life and security in the design of Bluetooth trackers, noting the absence of secure boot processes as a vulnerability.

The paper concludes that future developments in Bluetooth tracking technology will likely focus on enhancing security features. This is crucial as these devices become more integrated into the IoT ecosystem and subject to evolving privacy regulations. The research underscores the importance of addressing the security challenges presented by BLE trackers to balance functionality and security in next-generation systems.