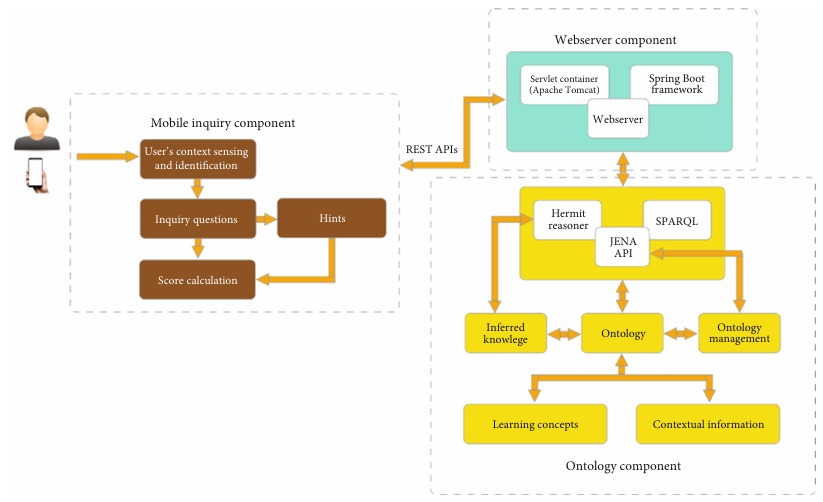
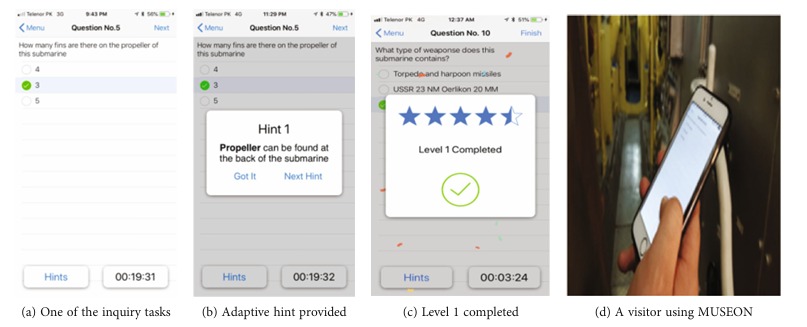
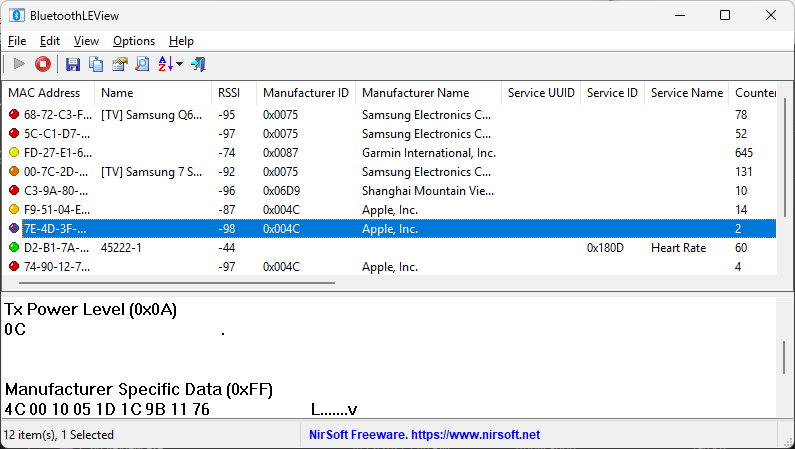
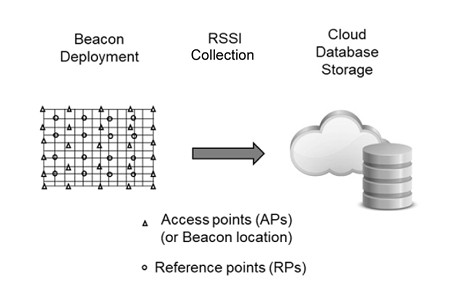
Logistics and supply chain operations are constantly seeking innovative technologies to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and security. Beacons have emerged as a transformative solution, enabling a range of applications across the industry. Here, we explore how beacons are revolutionising logistics and supply chain management.
Real-Time Asset Tracking
Beacons allow for the seamless tracking of assets, ranging from raw materials to finished products, as they navigate through the supply chain. This real-time visibility helps organisations monitor the location and movement of shipments, optimise logistics processes and mitigate risks of loss or misplacement. By providing continuous updates, businesses can make more informed decisions and ensure the smooth flow of goods.
Enhanced Inventory Management
Inventory accuracy is a critical component of supply chain efficiency, and beacons play a key role in automating stock level monitoring. By reducing reliance on manual checks, they provide up-to-date insights into inventory levels, enabling businesses to reorder efficiently and avoid issues like stockouts or overstocking. This automation not only improves operational efficiency but also reduces costs.
Safeguarding Perishable Goods
For goods that are sensitive to environmental conditions, such as food or pharmaceuticals, beacons equipped with sensors monitor variables like temperature, humidity and light exposure. This ensures that items remain within safe conditions throughout their journey, maintaining quality and compliance with industry standards. Such monitoring is particularly vital for the cold chain, where temperature control is paramount.
Warehouse Optimisation
Within warehouses, beacons track the precise location of items, simplifying the process of locating goods and optimising storage layouts. By automating stocktaking and improving workflow, beacons reduce the time spent searching for items and enhance overall warehouse efficiency. This leads to faster order fulfilment and better resource management.
Improved Fleet Management
Beacons also bring significant advantages to fleet management by tracking the position and condition of vehicles in real-time. This data allows logistics managers to optimise routes, improve dispatch accuracy, and maximise vehicle utilisation. Enhanced visibility of fleet operations translates into cost savings and improved delivery performance.
Predictive Maintenance for Equipment
The health of equipment such as forklifts, cranes and conveyor belts is crucial for uninterrupted operations. Beacons monitor key metrics related to equipment performance, enabling predictive maintenance that prevents breakdowns. By receiving timely alerts when maintenance is due, companies can reduce downtime and extend the life of their machinery.
Ensuring Worker Safety
In large logistics facilities, beacons are used to monitor the location of personnel. This allows managers to identify potential hazards and respond to incidents promptly. By providing alerts when workers enter restricted or high-risk areas, beacons contribute to a safer work environment and help mitigate accidents.
Supporting Cold Chain Logistics
Cold chain logistics, essential for products like food and medicine, relies heavily on temperature control. Beacons provide continuous environmental monitoring, ensuring that goods are stored and transported under the correct conditions. This safeguards product quality and maintains compliance with stringent industry standards.
Enhancing Cargo Security
Cargo security is a top priority in logistics, and beacons offer robust solutions by tracking goods within secure zones and sending alerts if items are moved without authorisation. This level of monitoring reduces the risk of theft and bolsters security protocols, particularly for high-value shipments.