A new study (pdf) explores optimising Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacon-based indoor positioning systems using support vector regression (SVR). It addresses the challenge of accurately identifying building occupants’ locations in real time, a critical requirement for applications such as emergency evacuations and asset tracking. Traditional methods, including trilateration and RSSI-based techniques, can face limitations like signal interference and non-line-of-sight issues.
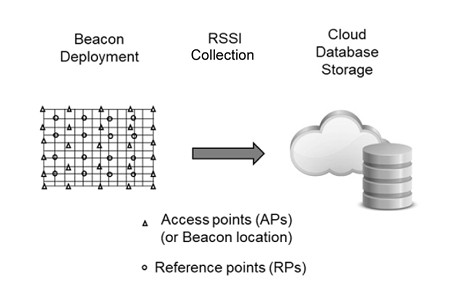
The research adopts a fingerprinting method that uses pre-trained SVR models to improve positioning accuracy. BLE beacons, which are cost-effective and energy-efficient, were deployed across a controlled environment, and extensive RSSI data was collected and pre-processed. The model’s hyperparameters were fine-tuned to achieve optimal performance. Experimental results demonstrated a significant improvement in accuracy, with the lowest root mean squared error (RMSE) recorded as 0.9168 feet.
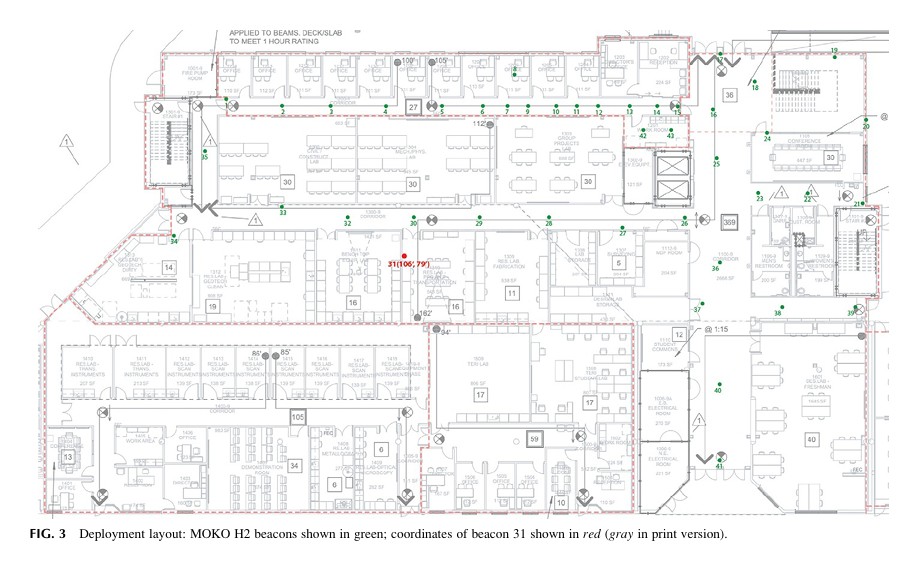
The findings underscore the potential of machine learning, particularly SVR, in enhancing the reliability of indoor positioning systems. This study provides a benchmark for future research, highlighting its practical applications in emergency scenarios and the advantages of BLE technology in such implementations.