Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons transmit a radio signal at regular intervals, powered by small batteries. The batteries need periodic replacement that can be time-consuming and costly when a large number of beacons are in use. There’s a new paper from Rzeszów University of Technology, Poland on Bluetooth Low Energy Beacon Powered by the Temperature Difference.
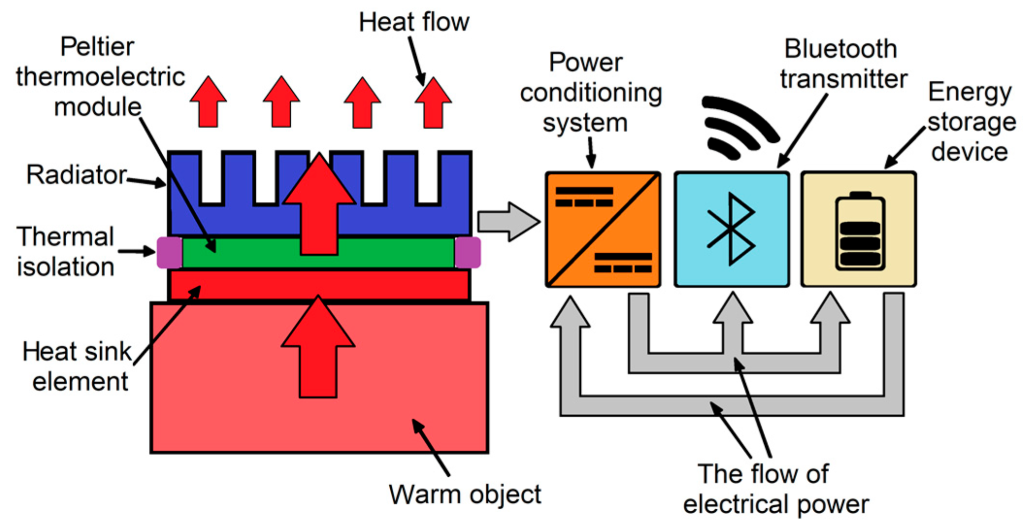
The paper proposes a power source that gathers energy through the Peltier effect. As temperature differences between two surfaces are present in most environments, the authors evaluated this energy source’s effectiveness in powering the beacons through measurements and simulations. They measured the beacon’s power supply demand in different modes and examined the Peltier module under different loads and temperature differences.
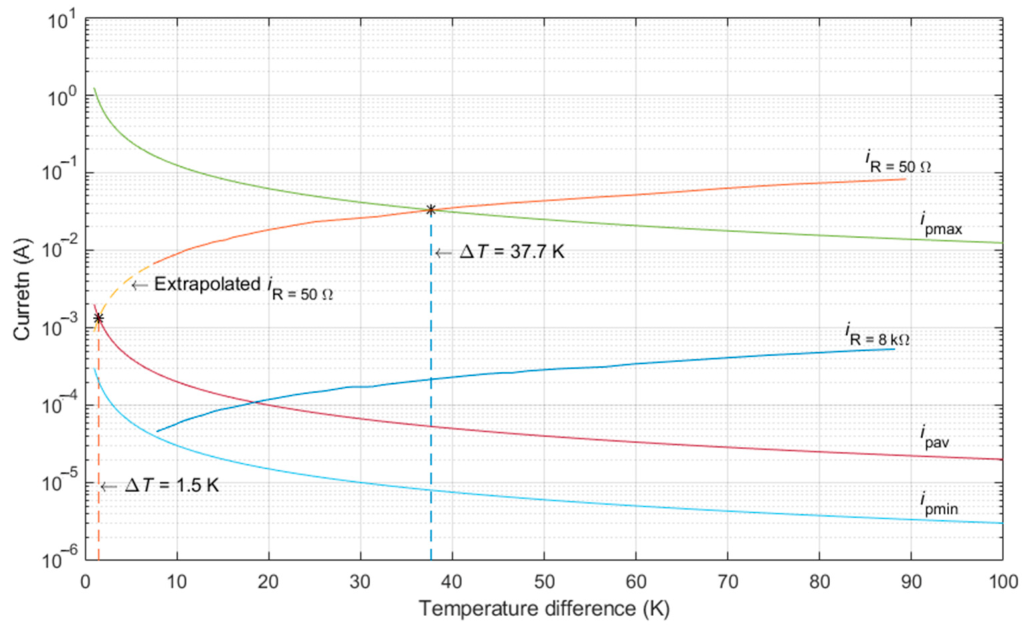
Based on the data gathered, they defined an energy conditioning system sufficient to power the beacon at a given temperature difference and developed a model of the proposed device. This solution eliminates the need for batteries, making the beacon maintenance-free.