There’s new research from University of Washington on BLE-Doubt: Smartphone-Based Detection of Malicious Bluetooth Trackers University of Washington (PDF).
Stalkers can hide Bluetooth beacons on targets’ clothing or in vehicles so as to monitor their locations. The researchers created an open-source method of detecting maliciously deployed Bluetooth beacons.
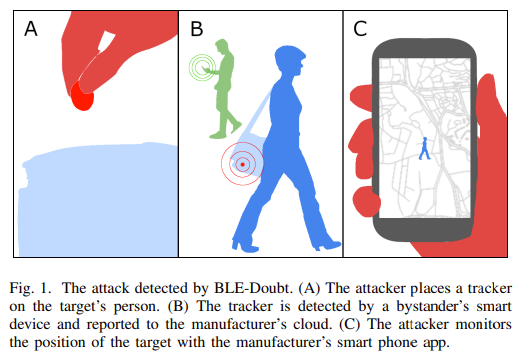
The algorithm detects malicious devices within a few minutes. The software scans for Bluetooth advertisements and stores a history so that an alert can be created if a beacon is following the same route as the user.
iBeacon, Altbeacon, Eddystone, Tile, Chipolo, Spot, and AirTag are all detected with AirTags the greatest challenge due to rotation of their MAC addresses between every two hours and once a day and their erratic and unpredictable advertising.
The app doing the scanning causes heavy smartphone battery use. The smartphone lost between 5% and 10% of its battery per hour during active scanning.